Overview:
This evaluation focused on a women's performance tank designed for athletic training, combining advanced knit construction with enhanced fiber treatments. Engineered with 50% cotton and 8% spandex, the garment features a wicking finish and SPF 30 protection. Its weft-knit structure, high-twist yarn, and balanced wale-to-course ratio create a product that is both performance-oriented and consumer-ready for seasonal wear.
Role and Responsibilities:
Role: Textile Performance Analyst
Responsibilities: My role involved assessing the tank’s performance across multiple serviceability dimensions, using lab testing and field standards to evaluate the material's chemical properties, comfort, resilience, and environmental durability. I also conducted an in-depth analysis of construction quality and finish integrity relative to price point and expected consumer use.
Technical Details and Innovation:
Fiber & Yarn Composition:
Materials: 50% cotton, 8% spandex blend offers a balance of softness, stretch, and moderate shape retention.
Yarn Structure: Warp and filling spun, single Z-twist, high-twist yarns contribute to improved tensile strength and visual texture. The fabric is weft-knit with a 1:1 ratio of wales to courses (64 each), producing a well-balanced, stable construction optimized for flexibility and breathability. The moisture management finish is designed to pull sweat away from the skin and speed up evaporation—helping maintain dryness and comfort during extended physical exertion. SPF 30 Rating: Adds value to outdoor training by increasing skin protection from UV exposure.
Durability Testing & Serviceability Insights:
Dimensional Stability: Post-treatment testing showed complete soil release, a key feature for consumers who frequently apply oils, lotions, or fragrances before activity. The garment's fibers demonstrated sensitivity to fluctuations in humidity and temperature. While the fabric maintains form in mild conditions, extended exposure to harsh climates could affect fit and shape. Rated a moderate 50 on water repellency tests. While the garment can resist light spills, it does not effectively block saturation in heavy rainfall or large-volume exposure. Natural fiber content contributed to a high pilling rate, which is expected but manageable depending on usage and laundering habits.
Fig. 1
Flammability & Colorfastness: The garment surpassed flammability benchmarks, ensuring safe performance under heat exposure. While durable under preparation and croaking tests, some results exceeded acceptable limits—suggesting potential dye migration with prolonged use.
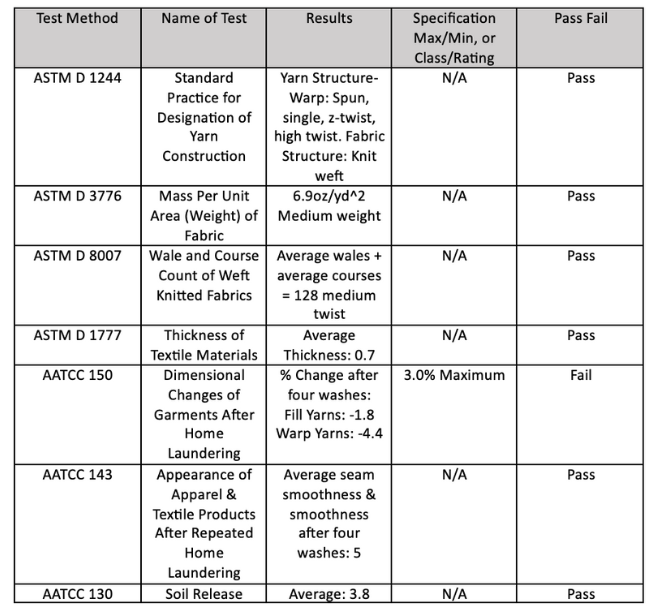
Test Methods:
To organize and showcase my data, I created charts including the test, test method, ASTM specification performance requirements, average test result, and whether the garment passed/failed all of the tests completed in the laboratory.
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Challenges Overcome:
Maintaining wicking functionality without compromising the hand feel of cotton proved complex. Finishes were selected based on polymer compatibility and wear-life testing. Construction integrity was carefully evaluated using the 4-Point System to ensure consistent quality over large production batches. Environmental durability—especially under varying humidity—remained a focal point for long-term user satisfaction
Test Methods - Not Omitted in Lab:
Fig. 4
ASTM D 6207-03(2019) Dimensional Stability of Fabrics to Changes in Humidity and Temperature.
-
This test method covers the determination of the dimensional stability of fabrics that are intended for use on panel and screen systems to cycle changes in humidity and temperature. Dimensional change growth and shrinkage data are collected for a specimen of fabric that is subjected to controlled cycles of specified relative humidity and temperature conditions.
-
Environmental test chamber, provision for automatic cycling of humidity and temperature conditions, visible humidity and temperature indicators, a continuous recording device, pointers, and a weight spring clamp
-
1. Place the prepared and precondition specimen vertically in the test chamber, that has been stabilized.
2. Attach a horizontal pointer to each specimen at the 900mm mark as indicated by the scale. Note observed discoloration, bubbling, or curling of the specimen and the stage of testing.
3. Over eight hours, increase the humidity and reduce the temperature. Record the pointer readings to the nearest 1mm, and the conditions.
4. Over the next 16 hours decrease the humidity level and raise the temperature. At the end of the period, record the pointer readings to the nearest 1mm in the conditions.
5. Repeat over the next 24 hours.
Fig. 5
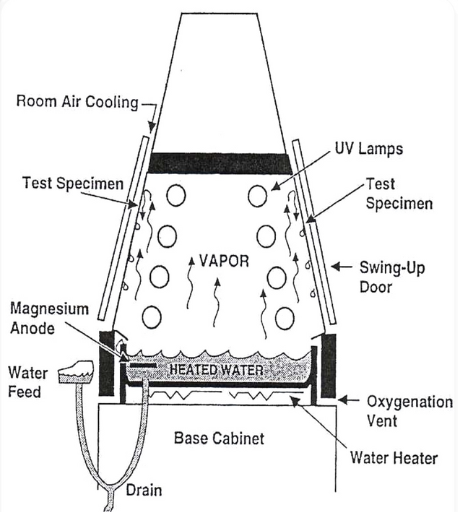
AATCC Test Method 186-2015 Weather Resistance: UV Light and Moisture Exposure
-
This test method provides a procedure for the exposure of textile materials of all kinds in the laboratory. Artificial weathering exposure apparatus, employing fluorescent UV lamps as a light source and using condensing humidity and warm water spray for wetting.
-
Test chamber, UV-A type fluorescent UV lamp, moisture system, condensation, water spray, black panel thermometer, specimen holders, and a test chamber location.
-
1. Mount the specimens in the frames which are supplied with the cabinet with the test surfaces facing the lamp. Ensure that the side, directly exposed to the radiant source is the one normally used as the face.
2. Program the device to achieve the required test conditions and operate the apparatus continuously within the limits specified.
3. Reposition specimen, at least five times during the duration of the test to minimize any effects from temperature or UV light variation. Flip horizontally by moving the two extreme right-hand specimen holders to the far left of the exposure area and sliding the remaining specimen holders to the right.